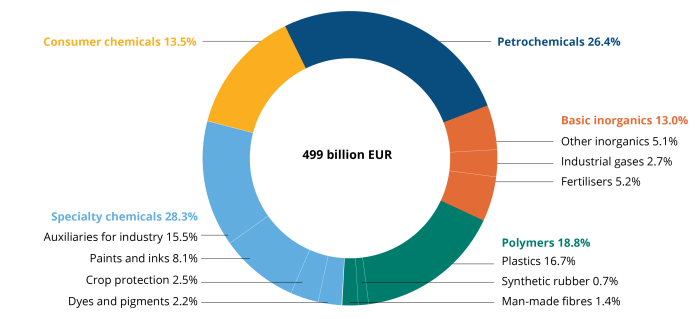
Exploring Chemicals used in the development and manufacturing of pharmaceutical products reveals the essential role that chemistry plays in creating effective medications. From the very first stages of drug development to the final product that reaches consumers, chemicals are fundamental in ensuring safety, efficacy, and quality. Understanding how these compounds work not only highlights their importance but also sheds light on the rigorous processes involved in bringing pharmaceuticals to market.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the intricate dance of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), excipients, solvents, and catalysts shapes the landscape of drug formulation. These diverse chemicals collaborate to enhance drug performance and patient outcomes, making them indispensable in the quest for innovative treatments.
Introduction to Chemicals in Pharmaceuticals
Chemicals play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry, serving as the building blocks for the development of medications. From the initial discovery of active ingredients to the final formulation of dosage forms, chemicals are integral throughout the entire process. Their diverse properties and behaviors enable scientists to create drugs that effectively target specific conditions and diseases.The importance of chemical compounds in ensuring drug efficacy and safety cannot be overstated.
These compounds are meticulously studied for their pharmacological effects, interactions, and potential side effects. The careful selection and combination of chemicals are essential to formulate drugs that not only provide therapeutic benefits but also minimize harmful reactions in patients. In this context, understanding the chemical makeup of pharmaceuticals is vital, as it directly influences the safety profile and therapeutic outcomes of the drugs.
Role of Active Ingredients
Active ingredients are the primary substances in a drug that produce the desired therapeutic effect. The selection of these ingredients is based on a multitude of factors, including their mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and patient safety. The following points highlight their significance:
- Active ingredients are responsible for the drug’s therapeutic effect, influencing how effectively a drug can alleviate symptoms or treat a condition.
- Each active ingredient undergoes rigorous testing to evaluate its safety profile, ensuring that it does not cause adverse reactions in patients.
- The potency and dosage of active ingredients are calculated based on extensive research and clinical trials, determining the appropriate administration for maximum efficacy.
Excipients in Formulation
Excipients are inert substances used alongside active ingredients to aid in the formulation of pharmaceutical products. They play a critical role in the overall development process by:
- Enhancing the stability of the active ingredients, ensuring that the drug maintains its efficacy over time.
- Facilitating the manufacturing process by improving the flow properties of powders or aiding in the compression of tablets.
- Encouraging patient compliance through the addition of flavoring agents or colorants that improve the palatability and appearance of the medication.
Importance of Chemical Stability
Chemical stability is a key consideration during the development of pharmaceutical products. It ensures that drugs maintain their potency and safety throughout their shelf life. The following aspects are vital to understanding chemical stability:
- Stability studies assess how drugs react under various environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light, determining their expiration dates.
- Degradation pathways of chemicals are studied to understand how active ingredients may break down over time, potentially forming harmful by-products.
- Formulation scientists utilize stabilizers and preservatives to enhance the shelf life of drugs without compromising their therapeutic efficacy.
“The efficacy and safety of pharmaceutical products are inextricably linked to their chemical composition and formulation strategies.”
Types of Chemicals Used
In the realm of pharmaceuticals, various chemicals play crucial roles in the development and manufacturing processes. Understanding these categories helps clarify their specific functions, which are essential to creating effective and safe drug products. From the core components that provide therapeutic effects to the supportive agents that facilitate the formulation, each chemical type contributes to the overall efficacy and safety of pharmaceutical products.Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients are two primary categories of chemicals utilized in drug development.
APIs are the substances in a pharmaceutical product responsible for its therapeutic action. They are biologically active and can directly affect the body or a specific disease state. Excipients, on the other hand, are inactive substances that serve as the vehicle or medium for the APIs. They can include fillers, binders, preservatives, and stabilizers, all of which help ensure the drug’s effectiveness, stability, and safety.
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
APIs are the heart of any pharmaceutical product; without them, a drug would lack its intended effect. Each API is specifically chosen based on its pharmacological properties and therapeutic benefits. Here are some key points regarding APIs:
- APIs can be derived from natural sources, such as plants and animals, or can be synthetically manufactured in laboratories.
- The potency of an API is typically measured in milligrams or micrograms, emphasizing the need for precision during formulation and manufacturing.
- Examples of common APIs include ibuprofen for pain relief, metformin for diabetes management, and atorvastatin for cholesterol control.
Excipients in Pharmaceutical Formulations
Excipients play a vital supporting role in the formulation of pharmaceuticals, ensuring that the APIs are delivered effectively. They can enhance the drug’s stability, bioavailability, and patient adherence. The importance of excipients can be categorized as follows:
- Functional excipients: These include agents that aid in drug formulation, such as binders that help hold the tablet together and disintegrants that facilitate the release of the API upon ingestion.
- Stabilizers: These excipients enhance the shelf life of products by preventing degradation during storage, particularly for sensitive APIs.
- Flavoring agents and colorants: These improve the palatability and appearance of medicines, particularly for pediatric formulations.
Role of Solvents, Reagents, and Catalysts
The manufacturing of pharmaceuticals often involves complex chemical reactions where solvents, reagents, and catalysts are crucial. Their roles can be summarized as follows:
- Solvents are liquids used to dissolve, extract, or suspend other substances. They can influence the solubility and reactivity of the API and are vital during the synthesis process. Common solvents include water, ethanol, and acetone.
- Reagents are chemicals that participate in a reaction to form a product. They can vary from simple acids or bases to more complex organic compounds, depending on the desired reaction.
- Catalysts speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They are often used to enhance yield and efficiency, making drug production more economical and environmentally friendly.
“The right combination of solvents, reagents, and catalysts can significantly reduce production times and costs, while also improving the purity of the final product.”
Chemical Synthesis Methods
In the pharmaceutical industry, chemical synthesis methods are essential for developing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). These methods encompass a range of strategies that chemists use to create complex molecules necessary for therapeutic purposes. The choice of synthesis method can significantly influence the efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness of a pharmaceutical product.Commonly used chemical synthesis methods include classical organic synthesis techniques as well as modern approaches that embrace advancements in technology and methodology.
Below are some of the primary methods utilized in pharmaceutical synthesis, each with its own set of advantages and examples.
Common Methods of Chemical Synthesis
Various synthesis methods are employed to create APIs, each tailored to the specific requirements of the molecule being produced. Here are some of the key methods:
- Stepwise Synthesis: This method involves synthesizing a compound in a sequential manner, where each step builds upon the previous one. An example includes the synthesis of penicillin, which is created through a multi-step process involving several chemical reactions.
- Retrosynthetic Analysis: This is a strategy where chemists break down a target molecule into simpler precursor structures to identify possible synthetic routes. The synthesis of the anticancer drug paclitaxel illustrates this approach, where complex natural product synthesis is derived from simpler starting materials.
- Continuous Flow Synthesis: This modern method utilizes a continuous flow reactor to produce chemicals in a more efficient and rapid manner. This technique has been successfully applied in the synthesis of various APIs, including certain antibiotics, reducing reaction times significantly.
- Solid-Phase Synthesis: Frequently used in peptide synthesis, this method allows for the chemical synthesis of peptides while attached to a solid support, facilitating easier purification. A notable example is the synthesis of peptide hormones like insulin.
Synthetic Pathways for Creating APIs
Synthetic pathways are critical in determining the feasibility and efficiency of pharmaceutical production. Each pathway is tailored to the unique characteristics of the target compound and often involves several intermediates.For instance, the synthesis of atorvastatin, a widely used cholesterol-lowering medication, uses a multi-step pathway starting from simple organic compounds. Each reaction is carefully controlled to produce the desired stereochemistry and functional groups necessary for biological activity.
Role of Green Chemistry in Synthesis
Green chemistry plays a pivotal role in reducing the environmental impact of chemical synthesis in pharmaceuticals. By promoting sustainable practices, green chemistry aims to minimize waste, prevent pollution, and enhance the efficiency of processes.Key principles of green chemistry include:
- Waste Prevention: Designing synthetic methods that minimize or eliminate waste helps reduce the environmental footprint of pharmaceutical production.
- Energy Efficiency: Employing methodologies that require less energy, such as microwave-assisted synthesis, can significantly lower the carbon footprint associated with drug synthesis.
- Use of Renewable Feedstocks: Utilizing raw materials from renewable sources instead of finite fossil fuels contributes to sustainability in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
By integrating green chemistry principles, pharmaceutical manufacturers can enhance their sustainability practices while maintaining the efficacy and safety of their products, ultimately benefiting both consumers and the environment.
Quality Control and Chemical Testing

Quality control and chemical testing are crucial steps in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) meet stringent standards of purity and potency. These processes are integral to maintaining safety and efficacy, ultimately protecting public health. Chemical testing begins with the selection of appropriate testing procedures that analyze the quality of pharmaceutical chemicals. The integrity of each batch of a drug is verified through various methods designed to assess its composition and concentration, making it essential for manufacturers to adhere strictly to established protocols.
Procedures for Testing Purity and Potency
Testing procedures are designed to determine both the purity and potency of pharmaceutical chemicals. Purity testing checks for the presence of contaminants or impurities, while potency testing assesses the strength and effectiveness of the substance. The following methods are commonly employed:
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): This technique is widely used for separating, identifying, and quantifying compounds in a mixture.
- Gas Chromatography (GC): Ideal for volatile substances, GC helps in analyzing the purity and composition of chemical samples.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): MS measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, providing detailed information about the molecular composition of samples.
- Infrared Spectroscopy (IR): Often used to identify functional groups in organic compounds, IR can indicate the presence of impurities.
- Titration: A classic method for quantifying the concentration of active ingredients by adding a reagent until a reaction endpoint is reached.
Standards Set by Regulatory Agencies
Regulatory agencies like the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and EMA (European Medicines Agency) establish rigorous quality standards for pharmaceuticals. Compliance with these standards ensures that products are safe for consumer use. Key guidelines include:
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): These practices Artikel the conditions under which pharmaceuticals must be produced, ensuring consistent quality.
- Pharmacopoeia Standards: Official compendiums like the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) provide detailed guidelines for testing methods and acceptable purity levels.
- ICH Guidelines: The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) provides comprehensive guidelines on quality, safety, and efficacy standards for drug development.
Comparison of Testing Methods
Different testing methods vary in application, speed, and sensitivity. The table below summarizes the characteristics of several key testing methods used in the pharmaceutical industry:
| Testing Method | Type | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC | Quantitative | High precision and sensitivity | Requires skilled operators |
| GC | Qualitative/Quantitative | Effective for volatile compounds | Not suitable for non-volatile substances |
| Mass Spectrometry | Qualitative/Quantitative | Detailed molecular information | High cost and complexity |
| Infrared Spectroscopy | Qualitative | Quick identification | Less precise with complex mixtures |
| Titration | Quantitative | Simplicity and cost-effectiveness | Time-consuming for large batches |
Maintaining rigorous quality control through chemical testing is not only a regulatory requirement but also a foundational aspect of pharmaceutical integrity.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework governing chemicals in pharmaceuticals is a vital component of ensuring public safety and efficacy in drug development and manufacturing. Regulatory bodies establish guidelines and standards that pharmaceutical companies must adhere to when using chemical substances in their products. These regulations help mitigate risks associated with the use of potentially harmful chemicals and ensure that medications meet the necessary quality and safety requirements.The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe play crucial roles in overseeing the approval and regulation of chemical substances used in pharmaceuticals.
They assess the safety, efficacy, and quality of drugs before they reach the market, thereby protecting public health. Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for pharmaceutical manufacturers to operate legally and maintain a good reputation in the industry.
Regulations Governing Use of Chemicals
Pharmaceutical companies must navigate a complex web of regulations that dictate how chemicals can be used in drug development and manufacturing. These regulations cover various aspects, including:
- Registration of chemical substances: Companies are required to register all chemical substances with regulatory bodies, detailing their intended use and safety data.
- Manufacturing practices: Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations set standards for production processes to ensure that drugs are consistently produced with quality and safety in mind.
- Labeling requirements: Accurate labeling of chemical substances is mandated to inform users about the potential risks and proper handling procedures.
- Environmental regulations: Companies must also comply with environmental laws concerning the disposal and management of chemical waste to minimize ecological impact.
Role of FDA and EMA in Approving Chemical Substances
The FDA and EMA are at the forefront of pharmaceutical regulation, each with specific mandates and processes for evaluating chemical substances:
- Preclinical testing: Before approval, drugs must undergo extensive preclinical testing, including safety and efficacy assessments involving chemical substances.
- Clinical trials: The FDA and EMA require detailed plans for clinical trials that assess how the chemical compounds perform in humans, ensuring their safety and effectiveness.
- New Drug Applications (NDAs) and Marketing Authorization Applications (MAAs): These applications are submitted to the FDA and EMA, respectively, and must include comprehensive data on the chemical substances and their effects.
- Post-market surveillance: Once approved, drugs are monitored for adverse effects related to their chemical components, with ongoing reporting requirements for manufacturers.
Compliance Requirements for Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
Compliance with regulatory demands is non-negotiable for pharmaceutical manufacturers. Companies must adhere to strict guidelines to avoid penalties and ensure continued market access:
- Regular audits: Manufacturers are subject to routine inspections to ensure compliance with GMP and other regulations.
- Documentation: Maintaining comprehensive records of chemical usage, processes, and quality control measures is crucial for regulatory review.
- Training: Continuous training programs for staff regarding compliance and safety protocols are necessary to foster a culture of quality assurance.
- Risk assessment: Companies must regularly conduct risk assessments related to chemical usage to identify potential hazards and implement mitigative measures.
Safety and Environmental Impact

The pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on various chemicals, many of which can be hazardous. Ensuring the safety of personnel and minimizing environmental impact are paramount in the handling and disposal of these substances. This section will analyze safety protocols for dealing with hazardous chemicals and discuss the related environmental considerations, including waste management practices.
Safety Protocols for Handling Hazardous Chemicals
Safety protocols are critical in pharmaceutical facilities, as they directly affect the well-being of workers and the surrounding community. These protocols often include comprehensive training for employees, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and strict adherence to standard operating procedures (SOPs). Key safety measures employed include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers are required to wear appropriate PPE such as gloves, goggles, masks, and lab coats to minimize exposure to hazardous chemicals.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): These documents provide crucial information on the handling, storage, and emergency measures related to specific chemicals.
- Regular Safety Training: Employees undergo periodic safety training to stay updated on best practices and emergency response protocols.
- Controlled Access Areas: Certain sections of the facility are restricted to authorized personnel only, reducing the risk of accidental exposure.
- Emergency Response Plans: Facilities have detailed plans that Artikel procedures to follow in case of chemical spills or other emergencies.
Environmental Considerations and Waste Management
The environmental impact of pharmaceutical chemicals necessitates effective waste management strategies. Facilities must comply with strict regulations governing the disposal of hazardous waste to prevent soil and water contamination. Considerations for managing chemical waste include:
- Segregation of Waste: Different types of waste must be separated at the source to ensure they are disposed of correctly.
- Recycling Programs: Some pharmaceutical companies have implemented recycling initiatives for solvents and other chemicals, which reduces waste and conserves resources.
- Waste Treatment Technologies: Advanced treatment methods like incineration and biological treatment are employed to neutralize hazardous waste before disposal.
- Compliance with Regulations: Companies must adhere to local and international regulations, such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), to ensure safe waste management.
Examples of Safety Measures in Pharmaceutical Facilities
Real-world examples illustrate how pharmaceutical companies implement safety measures effectively. For instance, major pharmaceutical manufacturers often invest in advanced ventilation systems that help minimize airborne contaminants. Additionally, companies like Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson utilize automated systems for handling hazardous substances, reducing human interaction and exposure. Facilities may also conduct regular audits and assessments to ensure compliance with safety regulations and to identify areas for improvement.
“The safety of employees and the environment is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a moral obligation that guides our operations.”
Innovations in Pharmaceutical Chemistry
The field of pharmaceutical chemistry is continuously evolving, with groundbreaking innovations that enhance drug development and improve therapeutic outcomes. Recent advancements have opened up new possibilities for the design and synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds, while also addressing challenges related to safety, efficacy, and environmental sustainability. This section will explore emerging trends in chemical research, the role of biotechnology, and novel compounds currently under investigation.
Emerging Trends in Chemical Research for Drug Development
Recent developments in pharmaceutical chemistry have paved the way for innovative approaches to drug design and synthesis. Key trends include the adoption of computational chemistry techniques, which facilitate the identification of potential drug candidates through virtual screening methods. Additionally, the rise of personalized medicine has led to a focus on developing drugs tailored to individual patient profiles based on genetic information.
Another significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into the drug discovery process. These technologies enhance the predictive capabilities of chemical interactions and streamline the identification of promising drug candidates, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional methods.
Impact of Biotechnology on Chemical Usage in Pharmaceuticals
Biotechnology has significantly transformed the landscape of pharmaceutical chemistry, particularly in the production of biologic drugs. This shift has resulted in the increasing use of biological molecules, such as monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins, which offer targeted therapeutic effects. Biotech advancements enable the development of more complex chemical structures that traditional synthetic methods may struggle to produce. Moreover, biomanufacturing processes have become essential for producing these biologics sustainably, minimizing the environmental footprint associated with chemical production.
Novel Chemical Compounds Currently Under Research for Pharmaceutical Applications
The search for new chemical entities is vital for advancing therapeutic options. Numerous novel compounds are currently being researched for their potential applications in various medical fields. Below is a list of some noteworthy compounds that showcase the diversity and innovation in pharmaceutical chemistry:
Modulator Compounds
These compounds target specific biological pathways to regulate disease processes, such as the development of small molecules that act on protein-protein interactions.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
These innovative therapeutic agents combine antibodies with cytotoxic drugs, allowing for targeted delivery to cancer cells, thereby minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
RNA-Based Therapeutics
Antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are being explored for their ability to modulate gene expression, providing new strategies for treating genetic disorders.
Next-Generation Anticoagulants
New chemical entities designed to more effectively prevent thrombosis while minimizing bleeding risks are currently in late-stage development.
Microbiome Modulators
Compounds that influence the gut microbiome are being investigated for their roles in treating metabolic diseases and contributing to overall health.Emerging innovations in pharmaceutical chemistry, particularly through the lens of biotechnology and novel compounds, are shaping the future of drug development. These advancements promise to enhance therapeutic efficacy and patient outcomes, while addressing the challenges of contemporary medicine.
Ending Remarks
As we’ve seen, the world of chemicals in pharmaceuticals is complex yet fascinating, driving both innovation and safety in drug development. By understanding the various types of chemicals, their synthesis, and the rigorous testing and regulatory frameworks in place, we can appreciate the immense efforts that go into creating effective and safe pharmaceutical products. The future of pharmaceutical chemistry promises exciting advancements, as emerging trends continue to shape the industry and enhance our collective health.
General Inquiries
What are active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)?
APIs are the active components in pharmaceutical products responsible for the intended therapeutic effect.
How are excipients different from APIs?
Excipients are inactive substances used as carriers for the active ingredients in a drug formulation.
What role do solvents play in drug manufacturing?
Solvents are used to dissolve chemicals and facilitate various reactions during the drug synthesis process.
What is green chemistry?
Green chemistry focuses on designing chemical processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances.
How do regulatory agencies ensure chemical safety in pharmaceuticals?
Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA set strict guidelines and testing protocols to evaluate the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical chemicals.