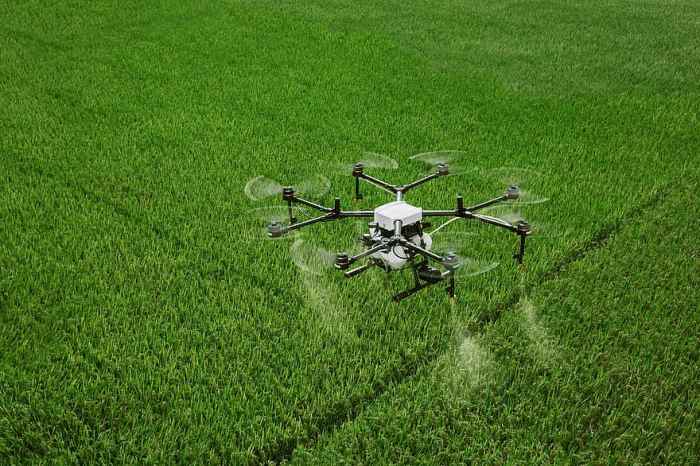
Drone Farming is making waves in the agricultural industry, offering innovative solutions to age-old farming challenges. This technology not only enhances efficiency but also transforms how farmers monitor and manage their crops. With the evolution of drone technology, the agricultural sector is experiencing a significant shift, where precision and sustainability take center stage.
From historical advancements to cutting-edge sensors, drone farming encapsulates a blend of tradition and modernity, paving the way for a new era in food production. As the industry evolves, understanding the benefits and applications of drone technology becomes essential for farmers looking to thrive.
Overview of Drone Farming
Drone farming is a revolutionary approach to agriculture that leverages unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to enhance farming efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. As the demand for food continues to rise globally, drone technology offers innovative solutions to help farmers manage their crops more effectively while minimizing environmental impact. This technology not only streamlines the farming process but also provides valuable data that can lead to better decision-making in agricultural practices.The evolution of drone technology in agriculture began in the early 2000s when UAVs were primarily used for military purposes.
Gradually, advancements in technology, such as miniaturization of sensors and improvements in battery life, allowed for the adaptation of drones for commercial use, including farming. Initially, drones were utilized for aerial photography and land surveying; however, as data analytics capabilities expanded, they became an essential tool for precision agriculture. Today, farmers use drones equipped with a variety of sensors to monitor crop health, assess soil conditions, and optimize resource management.
Primary Technologies in Drone Farming
Several key technologies underpin the effectiveness of drone farming, enabling farmers to gain insights into their fields and improve agricultural outputs. Understanding these technologies can help appreciate their role in transforming modern farming.The following technologies are integral to drone farming:
- Multispectral Imaging: This technology captures data at different wavelengths, providing insights into plant health, water stress, and nutrient levels. By analyzing these images, farmers can identify areas of concern in their fields and take corrective actions more swiftly.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR technology uses laser light to measure distances accurately. In agriculture, it helps create detailed topographical maps that can assist in planning irrigation systems and assessing land features.
- GPS and GNSS: Global Positioning System (GPS) and Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technologies allow for precise location tracking. This accuracy is crucial for mapping fields and applying agricultural inputs like fertilizers and pesticides uniformly.
- Thermal Imaging: Drones equipped with thermal cameras can detect temperature variations in crops, indicating areas that may require more water or are suffering from disease. This helps farmers to be proactive in their management strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies analyze data collected by drones to identify patterns and predict outcomes. AI and machine learning algorithms can provide actionable insights, such as predicting pest outbreaks or estimating crop yields.
By incorporating these technologies, drone farming not only enhances operational efficiency but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices that can lead to increased food security.
Benefits of Drone Farming

The adoption of drone technology in agriculture has ushered in a new era of farming, allowing farmers to optimize their operations like never before. With their advanced capabilities, drones are revolutionizing how agricultural tasks are conducted, leading to remarkable improvements in efficiency and crop management.Drones provide numerous advantages that contribute to enhanced agricultural productivity. They assist in precision agriculture, enabling farmers to monitor crops with high accuracy and perform tasks that were once labor-intensive and time-consuming.
This technology allows for quick assessment of crop health, soil conditions, and water needs, which can significantly improve yield and resource management.
Advantages of Using Drones in Agriculture
Drones offer a variety of benefits that can transform farming practices. Here are some key advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: Drones can cover large areas in a fraction of the time it would take traditional methods. This speed allows farmers to spend more time on other essential tasks while achieving comprehensive field assessments.
- Crop Monitoring: With the ability to capture high-resolution images and data, drones help in closely monitoring crop health, identifying issues like disease, pests, and nutrient deficiencies early on, which can lead to timely interventions.
- Data Collection: Drones collect valuable data that can be analyzed to optimize farming practices and improve decision-making. This data includes information on crop health, soil quality, and moisture levels.
- Precision Spraying: Drones equipped with spraying systems provide precise application of fertilizers and pesticides, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
- Accessibility: Drones can easily access difficult-to-reach areas of farmland, such as steep or muddy fields, providing thorough coverage that might be challenging with conventional methods.
Cost-Saving Aspects of Implementing Drone Technology
The introduction of drones into farming not only enhances operational efficiency but also offers significant cost-saving opportunities. Here are ways in which drone technology can lead to reduced expenses:
- Labor Costs: Automation of tasks traditionally requiring manual labor reduces the need for a large workforce, leading to lower labor costs.
- Input Reduction: By providing precise data on crop health and soil conditions, drones help in reducing the amount of fertilizers and pesticides needed, resulting in lower input costs.
- Fuel Savings: Drones are often more energy-efficient than traditional machinery, which can lead to decreased fuel expenses during field operations.
- Yield Improvement: By enabling better monitoring and care, drones can help increase crop yields, directly impacting profitability without a corresponding increase in operational costs.
Examples of Successful Drone Farming Practices
Several farmers and agricultural companies have already adopted drone technology with impressive outcomes. For instance, a vineyard in California implemented drones to monitor vine health and irrigation needs. By using this technology, they reported a 20% increase in overall yield, substantially enhancing their profit margins.Another example is a large corn farm in Iowa that utilized drones for planting and crop assessment.
The farm was able to reduce water usage by 30% by precisely targeting irrigation needs, leading to not only cost savings but also improved environmental sustainability.These examples illustrate how adopting drone technology in agriculture not only improves efficiency but also leads to better resource management and increased profitability, paving the way for a more sustainable future in farming.
Applications of Drones in Agriculture

Drones have transformed modern agriculture by providing innovative solutions for a variety of farming challenges. Their versatility allows farmers to collect data, monitor crops, and optimize resources, leading to improved yields and reduced costs. Understanding the specific applications of drones in agriculture is crucial for farmers looking to leverage technology effectively.Drones can be utilized in several key areas, each with its unique functionalities and benefits.
These applications range from crop monitoring and soil analysis to irrigation management, all of which contribute to more efficient farming practices.
Crop Monitoring
Crop monitoring is one of the primary applications of drones in agriculture. Using high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors, drones can capture detailed images and data of fields. This helps farmers assess plant health, growth patterns, and overall crop conditions.
- Drone technology enables real-time monitoring of crops, allowing for immediate responses to issues like pest infestations or disease outbreaks.
- Through thermal imaging, farmers can identify areas of water stress in crops, aiding in more efficient irrigation practices.
- Drones can cover large areas quickly, providing a comprehensive overview of the farm that would be time-consuming and labor-intensive to achieve on foot.
Soil Analysis
Soil analysis is integral to successful farming, and drones play a vital role in this process. Drones equipped with sensors can collect data on soil health and composition.
- They can map soil variations across a field, helping farmers to identify nutrient deficiencies, pH levels, and organic matter content.
- This data can inform precision agriculture practices, allowing for targeted interventions such as variable rate fertilization.
- Drones can also detect soil moisture levels, providing insights into the need for irrigation and helping to prevent water wastage.
Irrigation Management
Effective irrigation management is essential for maximizing crop yields, and drones facilitate this through advanced monitoring capabilities.
- Drones can analyze the distribution of water across fields, identifying spots that may be over or under-watered.
- By utilizing infrared imaging, they can assess crop stress and determine irrigation needs, helping to optimize water usage and improve crop health.
- Some drones come with the capability to assist in the automated application of fertilizers or pesticides in conjunction with irrigation systems, further enhancing efficiency.
Comparison of Different Drone Functionalities
Different drones offer various functionalities tailored to specific agricultural needs. Comparing these functionalities can help farmers select the right drone for their operations.| Drone Type | Functionality | Specific Agricultural Use ||——————|————————————————|——————————————————-|| Fixed-Wing Drones | Longer flight times and larger coverage areas | Ideal for large farms needing extensive monitoring || Multirotor Drones | Vertical take-off and landing, highly maneuverable | Best for detailed inspection of smaller fields or areas || Hybrid Drones | Combines fixed-wing and multirotor capabilities | Versatile use for various applications in agriculture |Each type of drone has its own advantages depending on the scale of the operation and the specific tasks required.
Case Studies in Drone Applications
Several case studies illustrate the practical applications of drones in agriculture, showcasing their effectiveness and efficiency.
- A vineyard in California implemented drones to monitor grape health, resulting in a 20% increase in yield. By precisely mapping vineyard conditions, the farmers were able to target interventions more effectively.
- In a corn production study in Iowa, drones were used to assess crop growth at different stages. The detailed imagery helped farmers apply fertilizers more accurately, reducing costs by 15%.
- A case in Brazil highlighted the use of drones for pest control in soybean fields. By pinpointing infestations accurately, farmers could minimize pesticide usage, resulting in less chemical runoff and improved sustainability.
These examples reflect the transformative power of drones in enhancing agricultural practices, leading to better productivity and environmental stewardship.
Challenges and Limitations of Drone Farming
Integrating drone technology into farming practices brings a set of challenges and limitations that farmers must navigate. While drones offer innovative solutions for many agricultural tasks, understanding these hurdles is crucial for effective implementation and maximization of benefits.
Common Challenges Faced by Farmers
Farmers encounter several obstacles when adopting drone technology. These challenges can stem from various sources, including financial constraints, operational difficulties, and training needs. Some of the key challenges include:
- High Initial Costs: The upfront investment for drones and related technology can be substantial, making it difficult for smaller farms to adopt.
- Technical Know-How: Many farmers may lack the necessary skills to operate drones effectively, necessitating training and support.
- Maintenance and Repair: Drones require regular maintenance and can be prone to repairs, adding to the operational costs.
Regulatory and Legal Issues
The legal framework surrounding drone usage in agriculture can be complex and varies by region. Farmers must be aware of the regulations governing airspace, privacy rights, and operational limits of drone use. Significant regulatory challenges include:
- Airspace Regulations: Farmers must comply with federal and state aviation regulations that dictate where and how drones can be flown, which can limit operational flexibility.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The collection of data using drones raises concerns about privacy and data ownership, necessitating compliance with data protection laws.
- Licensing Requirements: Obtaining necessary licenses for commercial drone operation can be a lengthy and complicated process, sometimes deterring farmers from utilizing the technology.
Technological Limitations and Potential Solutions
Drones come with technological limitations that can impact their effectiveness in agricultural applications. Addressing these limitations is essential for enhancing drone utility. Significant technological challenges include:
- Limited Battery Life: Most drones have a short flight time, typically ranging from 20 to 30 minutes, which can restrict their operational range and effectiveness. Solutions include investing in drones with longer battery life or developing battery swap systems.
- Weather Sensitivity: Drones are often not suitable for use in adverse weather conditions, such as rain or high winds. Utilizing drones with robust weather resistance features can mitigate this issue.
- Data Processing Challenges: The data collected by drones can be vast and complex, requiring substantial processing power. Employing advanced software solutions or cloud computing can streamline data analysis and interpretation.
Future Trends in Drone Farming
As agriculture continues to evolve, drone technology is set to play an increasingly pivotal role in farming practices. The next decade promises a surge in innovations and applications for drones that will reshape how food is produced, monitored, and managed. From enhanced data analytics to autonomous systems, the future of drone farming looks bright and full of potential.Emerging trends in drone technology are being driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics.
These technologies are enhancing the capabilities of drones, allowing for more precise data collection and analysis. As drone sensors become more sophisticated, they will be able to capture a wider range of data, including plant health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. By integrating this data with AI algorithms, farmers will gain deep insights that can inform their decision-making.
Innovations in Drone Technology
The field of drone farming is witnessing several key innovations that are changing the landscape of agriculture. These innovations include:
- Autonomous Drones: With the advancement of AI, drones are becoming increasingly autonomous, capable of conducting missions without human intervention. This reduces labor costs and allows for more efficient operations.
- Improved Imaging Technologies: High-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors are enabling drones to provide detailed insights into crop health and growth stages. This information is crucial for targeted interventions.
- Swarm Technology: The use of multiple drones working in coordination, or swarms, is enhancing the efficiency of large-scale farming operations. Swarms can cover vast areas quickly, collecting data or applying inputs uniformly across fields.
- Real-Time Data Processing: With better processing capabilities, drones can analyze data in real time, allowing farmers to act quickly on the information gathered and make timely decisions.
The evolution of drone farming over the next decade is likely to be marked by significant enhancements in data integration and predictive analytics. As agriculture becomes more reliant on data-driven decision-making, the integration of drones with other technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) will allow for more comprehensive monitoring systems. For instance, a farmer could use drones to monitor crop health and integrate that data with weather forecasts to optimize irrigation schedules, reducing water waste.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data
AI and big data are revolutionizing drone farming by enabling smarter, more efficient practices. The integration of these technologies allows for a more precise approach to agriculture, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected by drones to identify patterns and predict outcomes, improving crop management strategies. For example, a farmer could use predictive analytics to forecast yield based on historical data, weather patterns, and current soil conditions, allowing for better planning and resource allocation.Additionally, big data analytics can significantly enhance yield optimization.
By aggregating data from various sources, such as satellite imagery, drone footage, and sensor readings, farmers can make informed decisions that lead to increased productivity and sustainability.
“The future of agriculture lies in the integration of technology and data, with drones at the forefront of this transformation.”
Best Practices for Implementing Drone Farming
Implementing drone technology in farming can be transformative, enhancing efficiency and productivity. However, to maximize the benefits, farmers must approach this integration thoughtfully. This section Artikels practical guidelines and considerations to help farmers successfully incorporate drones into their agricultural practices.
Guidelines for Effective Adoption of Drone Technology
When looking to adopt drone technology, farmers should follow specific guidelines to ensure smooth integration. These considerations help to align drone usage with farming goals and operational strategies.
- Assess Farm Needs: Understand the specific needs of your farm, such as crop types, field size, and specific monitoring requirements.
- Research Drone Capabilities: Investigate different drone models and their functionalities, including payload capacity, battery life, and sensor types.
- Consider Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding drone usage, including licensing, flight restrictions, and data privacy laws.
- Evaluate Integration: Plan how drones will integrate with existing farm management systems or software for optimal results.
- Budget for Costs: Consider all costs associated with drone farming, including initial investment, maintenance, and training.
Checklist for Selecting Drones and Equipment
Selecting the right drones and equipment is crucial for successful drone farming. This checklist Artikels the key considerations to keep in mind during the selection process.
- Determine Flight Range: Evaluate the flying range necessary for your farm size to ensure thorough coverage without frequent recharging.
- Analyze Sensor Types: Choose drones equipped with the right sensors for your farming needs, such as multispectral cameras for crop health assessment.
- Inspect Durability: Select drones designed for agricultural environments, which can withstand weather changes and rough terrain.
- Review Software Compatibility: Ensure the drone’s software is compatible with data analysis tools that you plan to use for interpreting results.
- Check Support Services: Look for manufacturers that offer robust customer support, including repairs and training resources.
Training and Education Resources
To fully leverage the advantages of drone technology, farmers should prioritize training and education. This ensures they can effectively utilize drones and interpret the data collected.
- Online Courses: Many platforms offer courses on drone operation and data analysis specifically tailored for agriculture.
- Workshops and Seminars: Local agricultural extension services or universities often organize practical workshops focused on drone use in farming.
- Manufacturer Training: Drone manufacturers frequently provide training sessions for their equipment, which can be invaluable for new users.
- Peer Learning: Joining farming cooperatives or online forums allows farmers to share experiences and tips about drone farming.
Investing in knowledge is essential for farmers to maximize the benefits of drone technology, transforming their operations and boosting productivity.
Environmental Impact of Drone Farming
The integration of drones in agricultural practices presents a significant opportunity to enhance sustainability and minimize environmental impact. As farmers increasingly turn to technology, the potential for achieving environmentally friendly outcomes grows. Drones can enhance resource management and provide insights that lead to more sustainable practices in agriculture.Drones have become a pivotal tool in promoting sustainable agriculture. By utilizing drone technology, farmers can optimize their input usage, such as fertilizers and pesticides, thus reducing the overall chemical load on the environment.
This precision farming technique ensures that these substances are applied only where necessary, minimizing runoff and potential harm to surrounding ecosystems.
Reduction of Chemical Usage
The use of drones allows for targeted application of chemicals, which is essential in reducing environmental contamination. Here’s how drones facilitate this aspect:
- Variable Rate Application: Drones equipped with advanced sensors can monitor crop health in real-time. By analyzing data on growth stages and soil conditions, they can inform the precise amount of chemicals needed in specific areas.
- Spot Treatment: Instead of blanket spraying, drones can deliver chemicals to affected areas only, avoiding unnecessary exposure to healthy plants and reducing chemical use.
- Increased Efficiency: Drones can cover large areas quickly, providing timely applications that align with environmental conditions, further decreasing the likelihood of chemical runoff.
Drones also contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and ecosystem health. By minimizing the use of harmful chemicals and optimizing resource input, the surrounding flora and fauna can thrive. Studies show a correlation between reduced chemical inputs and improved soil health, which is vital for maintaining diverse ecosystems.
Long-term Implications on Biodiversity
The long-term implications of adopting drone farming practices can be profoundly positive for biodiversity and ecosystem health. Here are some noteworthy aspects:
- Soil Health Improvement: By reducing chemical usage and enhancing precision in nutrient application, soil health can improve significantly, leading to increased microbial activity and nutrient cycling.
- Habitat Conservation: Healthier ecosystems can support a diverse range of species, ensuring that agricultural practices do not encroach on natural habitats.
- Pollinator Support: Less chemical usage benefits pollinators like bees, which are crucial for crop production and biodiversity, promoting a balanced ecosystem.
Through these methodologies, drone farming represents a significant step towards more sustainable agricultural practices that prioritize environmental health. The shift towards precision farming not only supports farmers in maximizing yield but also paves the way for a future where agriculture coexists harmoniously with nature.
Economic Impact of Drone Farming
The adoption of drone technology in agriculture is not just a trend; it is transforming the economic landscape for commercial farmers. With the ability to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs, drones are becoming a vital tool in modern farming practices. The economic impact of drone farming extends beyond individual farms, influencing the overall agricultural economy and contributing to sustainable practices that yield financial benefits.
Economic Benefits of Drone Technology
Implementing drones in farming leads to several economic advantages. These benefits can significantly affect profitability and operational efficiency. Here are key points highlighting the economic benefits of drone technology:
- Cost Reduction: Drones can cut down labor costs by automating tasks such as crop monitoring, spraying, and mapping. Research indicates that drone usage can reduce labor costs by as much as 30%.
- Increased Efficiency: Drones can cover large areas in a fraction of the time it would take with traditional methods. This increased efficiency translates into higher productivity and more time for farmers to focus on other critical activities.
- Precision Agriculture: Drones enable precision agriculture, which optimizes resource use. This includes targeted pesticide application and precise fertilization, resulting in reduced input costs and higher yields.
Investment Costs Comparison
When comparing the investment costs of traditional farming methods to drone-supported practices, it is essential to consider both initial expenditures and long-term savings. Traditional methods often involve higher labor, fuel, and equipment costs, whereas drones represent an innovative solution that can save money over time.
- Initial Costs: The average cost of a drone suitable for farming can range from $1,500 to $25,000, depending on features and capabilities. In contrast, traditional equipment like tractors can cost tens of thousands of dollars with ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Studies indicate that farmers can expect a return on their drone investment in as little as three years due to increased yields and reduced operational costs.
Statistics and Projections
The drone farming industry is projected to experience significant growth, reflecting its economic impact. By 2025, the market for drone technology in agriculture is expected to reach approximately $6.5 billion, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30% over the next few years. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of precision agriculture and the need for sustainable farming practices.
“By integrating drones into their operations, farmers not only enhance their productivity but also contribute to the overall economic sustainability of the agricultural sector.”
The integration of drones in farming is leading to a paradigm shift in agricultural economics, with benefits that support both profitability and sustainability in the long run.
Last Point
In summary, Drone Farming presents a transformative opportunity for the agricultural landscape, merging technology with sustainable practices. As farmers embrace this innovation, the future of agriculture looks promising, with improved yields and reduced environmental impact. By navigating the challenges and harnessing the potential of drones, we can anticipate a more efficient and eco-friendly approach to farming.
Key Questions Answered
What are the main advantages of using drones in farming?
Drones increase efficiency by providing real-time data, enabling better crop monitoring and management, which can lead to higher yields.
Are there legal restrictions on drone usage in agriculture?
Yes, there are regulations that vary by region, including rules on where drones can be flown and required licenses for commercial use.
How much does it cost to implement drone farming?
The initial investment can vary widely depending on the technology used, but many farmers find significant long-term savings due to increased productivity.
Can drones help with pest control?
Absolutely! Drones can be equipped with sprayers for targeted pesticide application, reducing chemical usage and improving effectiveness.
What future trends are expected in drone farming?
Emerging trends include enhanced AI integration and big data analytics, improving decision-making and operational efficiency for farmers.