Energy Efficiency is more than just a buzzword; it’s an essential concept that shapes our modern lives. By optimizing how we use energy, we can significantly reduce our environmental impact, save money, and create healthier living spaces. This journey into energy efficiency will uncover its importance in fostering sustainability and highlight key statistics that reveal just how crucial this initiative has become.
As we delve deeper, you’ll discover the multifaceted advantages of improving energy efficiency, from economic benefits for both households and businesses to the positive effects on our health and the environment. Get ready to explore practical methods, innovative technologies, and inspiring case studies that demonstrate the power of energy efficiency in action.
Introduction to Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency refers to using less energy to provide the same service or achieve the same output. In modern society, the importance of energy efficiency cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in reducing energy costs, minimizing environmental impact, and enhancing energy security. By optimizing how we consume energy, we can contribute to a more sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come.The relationship between energy efficiency and sustainability is intertwined.
Higher energy efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption, which in turn lowers greenhouse gas emissions and natural resource depletion. This symbiosis helps mitigate climate change and promotes a healthier planet. As governments and organizations worldwide prioritize sustainability, energy efficiency serves as a fundamental strategy in achieving these goals.
Key Statistics on Energy Consumption and Efficiency Improvements
Understanding the current landscape of energy consumption and the potential for efficiency improvements is essential for making informed decisions. Here are some compelling statistics that highlight the significance of energy efficiency in our daily lives:
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), energy efficiency improvements could account for nearly 40% of the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions needed to meet global climate goals.
- The U.S. Department of Energy reports that energy-efficient appliances can save households $500 a year on energy bills, demonstrating the financial benefits of efficiency.
- Buildings represent approximately 40% of total energy consumption in the United States, indicating a substantial area where efficiency measures can lead to significant energy savings.
- Upgrading to energy-efficient lighting, such as LED bulbs, can reduce energy use for lighting by up to 75% compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
These statistics not only reveal the current energy consumption patterns but also underscore the potential impact of energy efficiency initiatives. By adopting energy-efficient technologies and practices, individuals and businesses alike can contribute to a more sustainable energy future while also benefiting economically.
Benefits of Energy Efficiency

Improving energy efficiency offers a wide range of benefits that extend beyond just saving money. Households and businesses alike can experience significant economic, environmental, and health advantages when they invest in energy-efficient practices and technologies.
Economic Advantages
The economic benefits of energy efficiency are substantial for both individuals and businesses. By making smart energy choices, households can reduce their utility bills, leading to more disposable income for other essentials or luxuries. Businesses also gain from lowering operational costs, which can enhance profitability. Here are some specific economic advantages:
- Reduced Energy Bills: Households can save an average of 25% on their energy costs by implementing energy-efficient appliances and practices.
- Increased Property Value: Energy-efficient homes often have higher market values, making them more attractive to potential buyers.
- Job Creation: The energy efficiency sector generates jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of energy-efficient products.
- Incentives and Rebates: Many governments offer financial incentives for energy efficiency upgrades, making it easier to invest in energy-saving technologies.
Environmental Benefits
The shift towards energy efficiency plays a critical role in reducing environmental impact. By conserving energy, we can significantly lower carbon emissions and preserve natural resources. Here are some key points that highlight the environmental benefits:
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: Energy-efficient practices can decrease greenhouse gas emissions, aiding in the fight against global warming.
- Conservation of Resources: Utilizing less energy translates to less reliance on fossil fuels, which helps conserve non-renewable resources.
- Reduced Air Pollution: Lower energy consumption can lead to improved air quality, benefiting ecosystems and human health.
- Sustainable Development: Energy efficiency supports sustainable practices that protect the environment for future generations.
Health Benefits
Energy-efficient buildings and appliances contribute to healthier living and working environments. These benefits extend beyond just comfort; they can also enhance overall well-being. Here’s how energy efficiency positively impacts health:
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: Energy-efficient systems often include better ventilation, reducing pollutants and allergens indoors.
- Enhanced Comfort: Proper insulation and energy-efficient systems maintain a consistent indoor temperature, promoting a comfortable living space.
- Noise Reduction: Many energy-efficient designs also include soundproofing features, leading to quieter, more peaceful environments.
- Reduced Exposure to Toxic Chemicals: Energy-efficient materials and appliances minimize the risk of exposure to harmful substances, fostering a healthier living space.
Investing in energy efficiency is not just about saving money; it’s about creating a sustainable and healthier future for ourselves and the planet.
Methods to Improve Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency in residential settings is crucial for reducing energy costs, minimizing environmental impact, and increasing overall comfort within the home. There are various methods to make residential spaces more energy-efficient, ranging from simple behavioral changes to the adoption of advanced technologies. Implementing these strategies not only helps in conserving energy but can also significantly enhance the quality of life for residents.One effective way to enhance energy efficiency is by upgrading to modern technology and using energy-efficient appliances.
These appliances are designed to consume less energy while delivering the same or even better performance compared to their traditional counterparts. Below are some methods that homeowners can employ to improve energy efficiency in their homes.
Techniques for Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Implementing the following techniques can lead to substantial energy savings in residential settings:
1. Upgrade Insulation
Enhancing insulation in walls, attics, and basements can prevent heat loss during winter and keep homes cooler in summer. Proper insulation reduces the workload on heating and cooling systems, leading to lower energy consumption.
2. Install Energy-Efficient Windows
Replacing single-pane windows with double or triple-glazed options can improve insulation and reduce heating and cooling costs. Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings can further enhance energy performance by reflecting heat back inside during colder months and keeping it out during warmer months.
3. Use Programmable Thermostats
These devices allow homeowners to set heating and cooling schedules, ensuring that energy is not wasted when the home is unoccupied. Smart thermostats can learn the homeowner’s habits and adjust temperatures accordingly for optimal efficiency.
4. Seal Air Leaks
Identifying and sealing gaps and cracks around doors, windows, and ducts can significantly reduce air leakage, which is responsible for a substantial amount of energy loss. Weatherstripping and caulking are simple solutions to this problem.
5. Adopt Energy-Efficient Lighting
Transitioning from incandescent bulbs to LED or CFL lighting can lead to considerable energy savings. These alternatives use a fraction of the energy and last much longer, reducing both energy bills and replacement costs.
Energy-Efficient Appliances and Their Benefits
Investing in energy-efficient appliances is a key strategy for improving energy efficiency at home. These appliances are designed to use less energy while maintaining high performance levels. Below is a list of common energy-efficient appliances and their benefits.Energy-efficient appliances often come with the ENERGY STAR label, indicating they meet strict efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
- Refrigerators: Modern energy-efficient refrigerators use 20% less energy than models made in the early 2000s. They often feature better insulation and advanced cooling technologies.
- Washing Machines: High-efficiency washers use 25% less energy and 33% less water than standard models, helping to save on utility bills and benefiting the environment.
- Dishwashers: Energy-efficient dishwashers use less water and energy per load compared to older models. They can save homeowners hundreds of dollars over their lifespan.
- Heat Pumps: These systems can be up to 300% more efficient than traditional heating systems, providing both heating and cooling solutions by transferring heat rather than generating it.
- LED Lighting: LEDs consume up to 80% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and have a longer lifespan, making them a cost-effective lighting solution.
Comparison of Traditional vs. Energy-Efficient Technologies
The following table presents a comparison between traditional and energy-efficient technologies across various sectors, illustrating the benefits and efficiency gains achievable by switching to more advanced options.
| Technology Type | Traditional Technology | Energy-Efficient Technology | Energy Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lighting | Incandescent Bulbs | LED Bulbs | Up to 80% |
| Heating | Conventional Furnaces | High-Efficiency Furnaces | 10-30% |
| Cooling | Old Air Conditioners | Energy-Efficient AC Units | 20-50% |
| Water Heating | Conventional Water Heaters | Tankless Water Heaters | 30-50% |
| Refrigeration | Old Refrigerators | ENERGY STAR Refrigerators | 20-50% |
Energy Efficiency in Commercial Buildings
Energy efficiency in commercial buildings is a critical aspect of sustainable development and cost management. As businesses seek to reduce operational costs and environmental impact, the implementation of energy-efficient practices becomes essential. This segment focuses on actionable strategies to enhance energy efficiency, the significance of building design and materials, and showcases successful energy-efficient projects in the commercial sector.
Strategies for Enhancing Energy Efficiency
There are several effective strategies that commercial properties can adopt to improve energy efficiency. These approaches not only help in reducing energy consumption but also contribute to significant cost savings over time.
- Implementing Energy Management Systems (EMS): Utilizing advanced software and tools to monitor and manage energy usage in real-time can lead to significant reductions in waste.
- Upgrading Lighting Systems: Switching to LED lighting and employing smart lighting controls can dramatically reduce electricity consumption, enhancing overall illumination quality.
- Utilizing Smart Thermostats: These devices facilitate automated heating and cooling schedules that adjust based on occupancy patterns, leading to optimal energy usage.
- Incorporating Renewable Energy Sources: Installing solar panels or wind turbines can decrease reliance on non-renewable energy, providing both environmental and economic benefits.
Role of Building Design and Materials
The design and materials used in commercial buildings significantly influence their energy efficiency. Thoughtful architectural decisions can lead to reduced energy consumption and improved comfort levels for occupants. Among the key considerations are:
Building Orientation
Positioning buildings to maximize natural light and minimize heat loss can lead to reduced energy needs for heating and cooling.
High-Performance Insulation
Using quality insulation materials in walls, roofs, and floors can prevent heat transfer, thereby maintaining temperature and reducing HVAC loads.
Energy-Efficient Windows
Installing double or triple-glazed windows with low-emissivity coatings can enhance thermal performance and reduce energy consumption significantly.
Successful Energy-Efficient Commercial Projects
Various commercial projects around the world have successfully implemented energy-efficient practices, leading to impressive outcomes. Notable examples include:
The Bullitt Center in Seattle
Known as one of the greenest commercial buildings globally, it features a rainwater harvesting system, solar panels, and composting toilets, resulting in minimal energy consumption and a net-zero energy footprint.
One World Trade Center in New York
This building employs a combination of advanced glass technology and energy-efficient HVAC systems, significantly reducing its overall energy demand while providing a comfortable working environment.
The Edge in Amsterdam
This office space uses an innovative energy system that includes geothermal heating and cooling, alongside smart sensors to optimize energy usage, resulting in a significant reduction in energy costs.These real-life examples illustrate the benefits of investing in energy efficiency, showcasing how commercial buildings can lead the way in sustainable practices while achieving economic advantages.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies play a crucial role in promoting energy efficiency across different sectors. By implementing various incentives and regulations, governments can drive both businesses and individuals towards adopting more energy-efficient practices. These efforts not only help reduce energy consumption but also contribute to environmental sustainability, economic growth, and job creation.One of the primary tools used by governments to encourage energy efficiency is the introduction of financial incentives.
These can take the form of tax credits, rebates, or grants aimed at reducing the upfront costs associated with energy-efficient technologies. For instance, many countries offer tax deductions for residential energy efficiency improvements, such as upgrading insulation, windows, and heating systems. Additionally, businesses may receive financial support for implementing energy-saving measures in their operations.
Types of Government Incentives
Understanding the various types of incentives available is essential for maximizing energy efficiency efforts. Here are some common incentives provided by governments:
- Tax Credits: Many governments offer tax credits for individuals or businesses that invest in energy-efficient technologies or renewable energy systems. This reduces the overall tax burden while encouraging green investments.
- Rebates: Cash rebates are often provided for purchasing energy-efficient appliances or upgrades, making these options more financially accessible to the public.
- Grants: Some government programs provide grants to support energy efficiency projects, especially for non-profit organizations and low-income households, ensuring equitable access to energy-saving improvements.
- Low-Interest Loans: Programs that offer low-interest loans help finance energy-efficient upgrades, allowing recipients to pay back the loan through the savings generated from reduced energy bills.
Regulations also significantly impact energy efficiency standards. Governments often set minimum efficiency requirements for appliances, vehicles, and buildings to ensure that energy consumption is minimized. These standards create a market for efficient products, thus driving innovation and competition among manufacturers. For example, the Energy Star program in the United States has established rigorous performance standards that help identify energy-efficient products across multiple categories.
Successful Policy Initiatives
Several successful policy initiatives have proved effective in enhancing energy efficiency on a broader scale. These initiatives not only showcase the potential of government action but also provide valuable lessons for future programs.One notable example is California’s Title 24 energy code, which sets mandatory energy efficiency standards for new buildings and major renovations. This initiative has led to substantial reductions in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, demonstrating the effectiveness of stringent regulations.
Additionally, the European Union’s Energy Efficiency Directive aims to achieve a 20% increase in energy efficiency by 2020, fostering collaboration across member states to share best practices and implement energy-saving measures.
“Strong governmental policies and incentives can catalyze the transition towards more energy-efficient practices, ultimately benefiting the environment and economy.”
Technological Innovations in Energy Efficiency
As the world moves toward a more sustainable future, technological innovations play a pivotal role in enhancing energy efficiency. These advancements not only reduce energy consumption but also contribute to a cleaner environment. With the integration of modern technologies, businesses and individuals can optimize their energy usage, leading to significant savings and a reduced carbon footprint.Emerging technologies have revolutionized how we approach energy efficiency, making it more accessible and effective.
This section explores several key innovations that are shaping the landscape of energy efficiency.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Several cutting-edge technologies are making waves in the energy efficiency sector. From smart appliances to advanced building materials, these innovations help streamline energy consumption. Notable examples include:
- Smart Thermostats: Devices like the Nest Learning Thermostat adapt to user behavior and optimize heating and cooling schedules, resulting in energy savings of up to 15%.
- LED Lighting: Compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, LED lights consume up to 80% less energy and have a longer lifespan, reducing both energy costs and waste.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Appliances certified with ENERGY STAR labels use less energy while maintaining performance, contributing to lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact.
Smart Grids and Energy Management Systems
Smart grids represent a significant leap forward in optimizing energy distribution and consumption. By utilizing digital technology, smart grids enhance the reliability and efficiency of electricity service. Energy management systems (EMS) play a crucial role in monitoring and controlling energy usage within buildings and industrial processes.Key features of smart grids and EMS include:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Users can track energy consumption patterns in real-time, allowing for quick adjustments to reduce waste.
- Demand Response Programs: These programs incentivize consumers to reduce or shift their power usage during peak demand periods, helping to prevent overloading the grid.
- Distributed Energy Resources: Smart grids facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, optimizing their use and increasing overall system efficiency.
Renewable Energy Technologies Enhancing Efficiency
Renewable energy technologies are integral to improving energy efficiency across various sectors. By harnessing natural resources, these technologies not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also enhance overall energy efficiency. Examples include:
- Solar Photovoltaics (PV): Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, providing a clean energy source that can power homes and businesses.
- Wind Turbines: Wind energy harnesses kinetic energy from wind, converting it into electricity with minimal environmental impact.
- Geothermal Systems: Utilizing the Earth’s natural heat, geothermal systems provide efficient heating and cooling options, significantly lowering energy consumption in buildings.
Innovations in energy efficiency are transforming how we consume and manage energy. By embracing these technological advancements, individuals and organizations can significantly contribute to a more sustainable future while enjoying the benefits of reduced energy costs and enhanced performance.
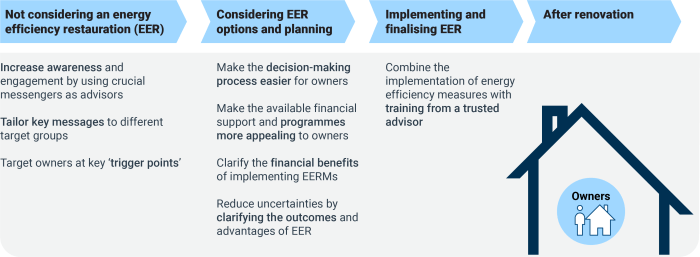
Challenges and Barriers to Energy Efficiency
Implementing energy-efficient practices presents a range of challenges for both individuals and organizations. These obstacles can stem from various economic, behavioral, and infrastructural factors that hinder the adoption of energy-saving measures. Understanding these barriers is essential for developing effective strategies to promote energy efficiency.One of the foremost barriers to energy efficiency is economic constraints. Many individuals and companies may lack the upfront capital required for energy-efficient upgrades, even if the long-term savings are evident.
Behavioral factors also play a significant role; resistance to change and a lack of awareness about energy efficiency benefits can prevent action. Additionally, infrastructural barriers, such as outdated systems and limited access to technological innovations, can further complicate efforts to enhance energy efficiency.
Economic Barriers
Economic limitations often serve as the primary obstacle to energy efficiency. Many individuals and organizations face challenges such as high initial costs, limited budgets, and fluctuating energy prices. These factors can discourage investment in energy-efficient technologies and practices.
- High Initial Costs: Energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and HVAC systems often have higher upfront costs. The perceived expense can dissuade potential buyers, even when long-term savings are forecasted.
- Budget Constraints: Small businesses and low-income households particularly struggle to allocate funds for energy efficiency projects, leading to a focus on immediate expenses rather than long-term benefits.
- Inconsistent Energy Prices: Fluctuations in energy prices can create uncertainty, making it difficult for businesses to justify investments in energy efficiency that may not show immediate returns.
Behavioral Barriers
Behavioral barriers encompass attitudes and perceptions that influence decision-making regarding energy efficiency. These include resistance to change, lack of awareness, and perceived inconvenience.
- Resistance to Change: Many individuals and organizations are accustomed to traditional practices and may resist adopting new, energy-efficient technologies due to uncertainty or fear of the unknown.
- Lack of Awareness: A significant portion of the population is unaware of the benefits of energy efficiency, leading to missed opportunities for cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
- Perceived Inconvenience: Energy-efficient products may be seen as more complex or less convenient, deterring users from making the switch.
Infrastructural Barriers
Infrastructural challenges can significantly hinder the implementation of energy efficiency measures. These barriers often stem from outdated systems, regulations, and a lack of access to innovative technologies.
- Outdated Infrastructure: Many buildings and facilities are equipped with older systems that are not conducive to energy efficiency, requiring substantial investment to upgrade.
- Regulatory Constraints: Local, state, and national regulations can complicate or slow the implementation of energy-efficient technologies, particularly in older buildings where compliance with modern standards can be challenging.
- Lack of Access to Technology: In certain areas, especially rural or economically disadvantaged regions, access to the latest energy-efficient technologies can be limited, stalling progress toward greater efficiency.
Strategies to Overcome Barriers
Addressing the challenges to energy efficiency requires targeted strategies that cater to the specific barriers discussed.
- Financial Incentives: Governments and organizations can provide grants, rebates, and low-interest loans to help alleviate the burden of upfront costs associated with energy efficiency upgrades.
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives to raise awareness about the benefits of energy efficiency can encourage individuals and businesses to adopt more sustainable practices.
- Support for Technological Innovation: Investing in research and development can lead to more affordable and accessible energy-efficient solutions, making them easier to adopt for a wider audience.
“Overcoming the barriers to energy efficiency is not just about technology; it’s about fostering a culture of sustainability and awareness in our communities.”
Case Studies of Energy Efficiency
The successful implementation of energy efficiency projects can significantly reduce energy consumption and costs while contributing to environmental sustainability. Examining detailed case studies reveals valuable insights into practical applications, lessons learned, and the overall impact of energy-efficient practices across various sectors.One of the most effective ways to understand energy efficiency is through real-world examples. These case studies illustrate diverse strategies employed by different organizations and sectors to enhance energy performance.
They also shed light on the measurable outcomes and the practical challenges faced during implementation, providing a roadmap for future initiatives in energy efficiency.
Successful Energy Efficiency Projects
Several notable projects have demonstrated significant success in implementing energy efficiency measures. Below are three detailed case studies: The Empire State Building, New York City: This iconic building underwent a comprehensive energy retrofit that included installing high-performance windows, upgrading heating and cooling systems, and improving insulation. The updates led to a reduction in energy consumption by 38%, resulting in annual savings of $4.4 million.
2. Google’s Mountain View Campus
Google has committed to achieving 100% renewable energy for its global operations. Its headquarters features energy-efficient designs, such as natural ventilation, a green roof, and advanced building management systems. The company reported a 30% reduction in energy use, contributing to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint. The Bullitt Center, Seattle: Known as one of the greenest commercial buildings in the world, the Bullitt Center incorporates photovoltaic panels, rainwater harvesting, and energy-efficient systems.
The building produces more energy than it consumes, achieving a net-zero energy status. Its design serves as a model for future sustainable architecture.
Lessons Learned and Implications
The case studies highlighted provide several key takeaways that can guide future energy efficiency projects:
Comprehensive Planning is Crucial
A thorough analysis before implementation helps identify the most effective measures to adopt and potential pitfalls.
Stakeholder Engagement
Involving all stakeholders, from management to employees, fosters a culture of sustainability and ensures successful project adoption.
Regular Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous assessment of energy usage helps in identifying areas for improvement and maintaining accountability.
Summary of Outcomes and Key Metrics
To better understand the impact of these case studies, the following table summarizes key outcomes and metrics:
| Project | Energy Reduction (%) | Annual Savings ($) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empire State Building | 38% | $4.4 million | High-performance windows, upgraded HVAC |
| Google’s Mountain View Campus | 30% | Not publicly disclosed | Natural ventilation, green roofs |
| Bullitt Center | Net-zero | Not applicable | Photovoltaics, rainwater harvesting |
Future Trends in Energy Efficiency
The future of energy efficiency is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and the integration of renewable energy sources. Over the next decade, we can expect significant innovations in how we approach energy consumption and efficiency, aiming to create a more sustainable environment.As society becomes increasingly aware of the impacts of energy use on the environment, consumer behavior is likely to shift toward prioritizing energy-efficient solutions.
This shift will not only affect purchasing decisions but will also influence the development and adoption of new technologies and practices.
Predicted Innovations in Energy Efficiency
Several key innovations are anticipated to shape the landscape of energy efficiency in the coming years. These developments are crucial for addressing global energy challenges while promoting sustainability.
- Smart Grids: The integration of smart grid technology will enable real-time monitoring and management of energy use, allowing consumers to optimize their energy consumption based on demand. This data-driven approach will facilitate more efficient energy distribution and reduce wastage.
- Energy Management Systems (EMS): Advanced EMS will provide businesses with the tools to analyze energy data, identify inefficiencies, and implement strategies to reduce usage. Such systems can help in tracking performance and setting benchmarks for energy savings.
- Home Automation: The rise of smart home devices will lead to increased energy efficiency in residential settings. Products such as smart thermostats, energy-efficient appliances, and automated lighting systems can significantly reduce energy consumption through intelligent management.
- Building Retrofitting: Upgrading existing buildings with energy-efficient materials and technologies is expected to gain momentum. This includes installing better insulation, energy-efficient windows, and renewable energy sources such as solar panels.
Impact of Consumer Behavior on Energy Efficiency
Consumer choices play a pivotal role in driving the demand for energy-efficient products and services. As people become more eco-conscious, their preferences will influence market trends and promote the adoption of sustainable practices.The trend toward sustainability is reflected in various consumer behaviors, including:
- Preference for Energy Star-rated products, which are designed to consume less energy while providing the same or improved performance.
- Adoption of renewable energy solutions, such as solar panels and wind turbines, that not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also enhance energy independence.
- Participation in energy efficiency programs and initiatives, supported by government incentives and rebates, which encourage consumers to invest in home improvements that lower energy costs.
Integration with Emerging Energy Sources
The synergy between energy efficiency and renewable energy sources is vital for achieving a sustainable energy future. The integration of these two aspects can lead to a more resilient and environmentally friendly energy system.Key points regarding this integration include:
- Decentralized Energy Generation: With the rise of distributed energy resources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, there is a growing focus on energy efficiency at the local level. This allows for better energy management and reduced transmission losses.
- Battery Storage Solutions: The development of advanced battery technologies facilitates the storage of excess energy generated from renewable sources, enabling consumers to utilize this energy efficiently during peak demand times.
- Demand Response Programs: These programs incentivize consumers to reduce or shift their energy use during peak periods, contributing to energy efficiency while enhancing grid stability.
Last Word
In conclusion, embracing energy efficiency not only benefits your wallet but also contributes to a sustainable future. By understanding the methods, policies, and technologies that drive energy efficiency, you can play a vital role in the global effort to conserve resources and reduce carbon footprints. Let’s make informed choices today for a cleaner, greener tomorrow!
Commonly Asked Questions
What is energy efficiency?
Energy efficiency refers to using less energy to provide the same service or achieve the same outcome, ultimately leading to reduced energy consumption and environmental impact.
How can I improve energy efficiency at home?
You can improve energy efficiency at home by using energy-efficient appliances, sealing windows and doors, adding insulation, and utilizing smart home technologies.
Are there any government incentives for energy efficiency improvements?
Yes, many governments offer tax credits, rebates, and grants for upgrading to energy-efficient systems and appliances, encouraging homeowners and businesses to invest in sustainability.
What are some common barriers to adopting energy-efficient practices?
Common barriers include high upfront costs, lack of awareness, and insufficient infrastructure or support for implementing energy-efficient solutions.
How does energy efficiency impact health?
Energy-efficient buildings often improve indoor air quality and comfort, which can lead to better overall health for occupants.