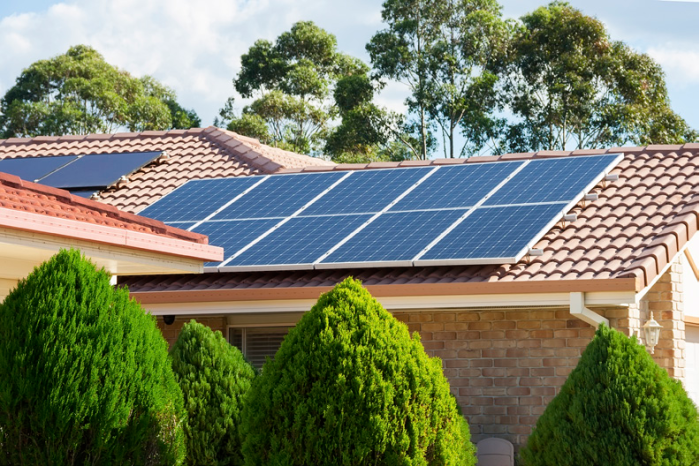
Have you ever thought about harnessing the sun’s power to save on energy bills and help the planet? Solar Panel Installation is not just a trend; it’s a smart move toward renewable energy that benefits both the environment and your wallet. With increasing awareness of climate change, solar energy offers a sustainable solution to meet our energy needs while reducing our carbon footprint.
By switching to solar, homeowners and businesses can enjoy a range of economic benefits, including lower utility bills and potential tax incentives. Understanding how solar panels work and the installation process can empower you to make informed decisions about embracing this eco-friendly technology.
Introduction to Solar Panel Installation
Solar panel installation refers to the process of setting up photovoltaic (PV) panels to harness solar energy for electricity generation. This practice plays a crucial role in the shift towards renewable energy sources, providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. As the world grapples with the impacts of climate change, solar energy emerges as a pivotal solution that not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes energy independence.The environmental benefits associated with solar energy are significant.
By converting sunlight into electricity, solar panels help decrease reliance on coal and natural gas, which are key contributors to air pollution and global warming. The adoption of solar energy can lead to a substantial reduction in carbon footprints, potentially eliminating millions of tons of CO2 emissions annually. Furthermore, solar energy production requires minimal water usage compared to traditional power generation methods, making it a water-efficient energy source.
Economic Advantages of Solar Energy
The economic benefits of installing solar panels extend beyond just saving on utility bills. Homeowners and businesses can experience a range of financial incentives and advantages, contributing to overall cost savings and long-term investment returns. Here are some key economic aspects to consider:The initial investment in solar technology can yield significant returns over time. Many regions offer tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives that can significantly offset installation costs.
These incentives encourage the adoption of solar energy and bolster the local economy.
- Tax credits: Federal investment tax credits (ITC) provide homeowners and businesses with up to 26% of the installation costs back on their federal taxes, making solar more affordable.
- Increased property value: Homes equipped with solar energy systems often see an increase in property value, making them more attractive in the real estate market.
- Long-term savings: With solar energy, electricity bills typically drop significantly, sometimes by 50% or more, leading to substantial savings over the lifespan of the system, which can exceed 25 years.
- Job creation: The solar industry has been a significant source of job creation, providing employment opportunities in installation, maintenance, and manufacturing.
By investing in solar panel installation, both residential and commercial property owners can create a sustainable energy future while also enhancing their economic standing. The financial and environmental benefits make solar energy not just a responsible choice but also a savvy economic decision.
“Solar energy is the ultimate in renewable energy sources, providing an opportunity for economic growth while protecting our environment.”
Types of Solar Panels
Solar panels come in various types, each designed to serve specific needs and preferences. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision regarding which solar panel technology is best suited for your home or business. The three primary types of solar panels available on the market today are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single crystal structure, which gives them a distinctive black appearance. These panels are known for their high efficiency and space-saving features. Their efficiency rates typically range between 15% to 22%, making them one of the most efficient solar panel types available.
- Efficiency: Monocrystalline panels boast the highest efficiency, converting more sunlight into electricity compared to other types.
- Cost: They are generally more expensive due to the manufacturing process and the purity of silicon used, which results in higher performance.
- Suitability: Best suited for residential installations where roof space is limited and homeowners want maximum energy output.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels are composed of multiple silicon crystals melted together. They have a bluish hue and are typically less expensive than monocrystalline panels. The efficiency of polycrystalline panels usually falls between 13% to 16%.
- Efficiency: While they are less efficient than monocrystalline panels, they still offer a respectable performance.
- Cost: More affordable than monocrystalline panels, making them a popular choice for those on a budget.
- Suitability: Ideal for larger installations where space is not a constraint, as they require more area to produce the same amount of energy as monocrystalline panels.
Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are made using a variety of materials, including cadmium telluride and amorphous silicon. These panels are lightweight and flexible, allowing for easy installation on various surfaces. However, they generally have lower efficiency rates, ranging from 10% to 12%.
- Efficiency: Thin-film panels are the least efficient of the three types, which means they require more surface area to generate the same amount of electricity.
- Cost: They are typically the least expensive option, making them attractive for large-scale solar installations.
- Suitability: Best suited for applications where weight and flexibility are crucial, such as on rooftops that cannot support heavier panels or for portable solar solutions.
“Choosing the right type of solar panel depends on various factors, including your budget, available roof space, and energy needs.”
Planning for Solar Panel Installation
When it comes to installing solar panels, proper planning is essential for success. Not every location is suitable for solar panels, and understanding the factors that impact their efficiency can help ensure you make the right decision. This section discusses the key steps in assessing your location for solar panel installation and highlights factors that play a significant role in the process.
Assessing Location Suitability
Evaluating the suitability of your location for solar panel installation involves several steps. Start by examining the physical attributes of your property, including roof characteristics and environmental factors.One of the first things to consider is the roof orientation. Ideally, solar panels should be mounted on a roof that faces south in the Northern Hemisphere or north in the Southern Hemisphere, as this orientation allows for maximum sun exposure throughout the day.
Another critical aspect is shading. Nearby trees, buildings, or structures can cast shadows on your panels, reducing their efficiency. It’s important to assess how much shade your roof receives at different times of the day and throughout the year. Using tools like solar pathfinders or apps can assist in analyzing the sunlight exposure. Space availability is also crucial.
You need enough unshaded space on your roof or property to accommodate the solar panels you wish to install. On average, residential solar panel systems require about 400 to 800 square feet of roof space, depending on the system’s size and energy needs.Additionally, considering the structural integrity of your roof is essential. Older roofs may need reinforcement to support the additional weight of solar panels.
It’s advisable to consult with a professional to confirm that your roof can safely hold the system.
Preparation Checklist for Homeowners
Before moving forward with the installation, it’s beneficial to compile a checklist that Artikels necessary preparations. This can streamline the process and ensure that you have everything in order.Consider including the following items in your checklist:
Roof Inspection
Ensure your roof’s condition is suitable for installation and check for any necessary repairs.
Permitting and Regulations
Research local laws and regulations regarding solar installations, as some areas may require permits or have specific guidelines.
Energy Needs Assessment
Analyze your current energy consumption to determine the size of the solar panel system needed.
Consultation with Professionals
Schedule consultations with licensed solar contractors to receive quotes and further assessments.
Financial Considerations
Investigate financing options, rebates, and incentives that may be available in your area.
“Proper planning and preparation are essential for maximizing the benefits of solar energy.”
Following these steps will help you assess the suitability of your location for solar panel installation and ensure you are well-prepared for the installation process ahead.
Installation Process
Installing solar panels on a residential roof is an exciting venture that can lead to significant energy savings and a reduced carbon footprint. Understanding the installation process is essential for homeowners looking to make the switch to solar energy. This guide will walk you through each step of the installation process, from initial assessments to the final setup.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
The installation of solar panels involves several key steps that ensure the system is efficient and safe. The following steps Artikel the process from start to finish:
- Site Assessment: A qualified installer will evaluate your roof’s structure, orientation, and shading to determine the best solar system setup.
- System Design: Based on the assessment, a custom design for the solar panel layout is created, including the type and number of panels needed.
- Permits and Approvals: Before installation begins, necessary permits must be obtained from local authorities to comply with regulations.
- Mounting Preparation: The installer prepares the roof by placing mounts securely attached to the rafters to ensure stability.
- Panel Installation: Solar panels are then mounted onto the prepared structure, connected securely to the electrical system.
- Wiring and Inverter Setup: Electricians will connect the panels to an inverter that converts direct current (DC) from the panels to alternating current (AC) for home use.
- Final Inspection: An inspection is conducted to ensure everything is installed correctly and safely, followed by the activation of the system.
Installation Method Comparison
Choosing the right installation method is crucial depending on your property’s space and orientation. Below is a comparison of roof-mounted vs. ground-mounted solar systems.
| Feature | Roof-Mounted | Ground-Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Space Efficiency | Utilizes existing roof space, leaving yard available. | Requires a dedicated area of land, may take up more space. |
| Installation Cost | Generally lower due to fewer materials needed for mounts. | Higher installation costs due to the foundation and mounting system. |
| Accessibility | More difficult to access for maintenance and cleaning. | Easier access for maintenance and cleaning tasks. |
| Aesthetics | Less visible from ground level, blends with the building. | More visible, may impact yard aesthetics. |
| Performance | Can be affected by shading from nearby structures. | Can be positioned for optimal sun exposure, reducing shading issues. |
Safety Precautions During Installation
Safety is paramount when installing solar panels, as the process involves working at heights and dealing with electrical components. Implementing the following safety measures can prevent accidents and ensure a smooth installation:
Always use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as helmets, gloves, and harnesses.
Ensure that the work area is free from hazards and that ladders and scaffolding are stable and secure.
Disconnect all electrical power during installation to prevent shock hazards.
Follow all local and national electrical codes and safety regulations throughout the installation process.
Employ experienced installers who understand the risks and best practices associated with solar panel installation.
Costs and Financing Options

Investing in solar panel installation can seem overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding the associated costs and financing options available. However, breaking down the expenses and exploring financial alternatives can help you make an informed decision, easing the transition to renewable energy. When considering solar panel installation, the costs can vary significantly based on multiple factors, such as the system size, type of panels, installation complexity, and local labor rates.
A typical residential solar system in the United States may range from $15,000 to $30,000 before any incentives. It’s essential to account for potential savings through tax credits and rebates, which can substantially reduce the initial investment.
Typical Costs of Solar Panel Installation
Understanding the breakdown of costs involved in solar panel installation can provide clarity when budgeting for your solar project. The primary cost components include:
- Solar Panels: The panels themselves typically make up about 40% of the total cost. Prices for solar panels have decreased over the years, averaging between $0.80 to $2.50 per watt.
- Inverters: These are crucial for converting the direct current (DC) electricity produced by the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity used in homes. They account for approximately 20% of the system cost.
- Installation: Labor charges can vary widely based on the complexity of the installation. Typically, installation costs can account for around 15-20% of the total project cost.
- Permits and Fees: Local regulations may require various permits, adding to upfront costs. These can range from $500 to $2,000, depending on location.
- Monitoring Systems: Optional systems to monitor energy production can add to costs, generally ranging from $300 to $1,000.
Financing Options Available
There are several financing options available for homeowners looking to install solar panels, each with its own benefits and considerations. Understanding these can help you choose the best fit for your financial situation.
- Solar Loans: These loans allow you to finance your solar system upfront, enabling you to own the system and benefit from tax incentives. Interest rates can range from 3% to 7%.
- Leases: With a solar lease, you pay a fixed monthly fee to use the solar system installed on your property without owning it. You’ll benefit from lower energy bills, but won’t receive tax credits.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Similar to leases, in a PPA, you pay for the electricity generated by the solar panels, often at a lower rate than your local utility. While you don’t own the system, it provides immediate savings on your energy bill.
Long-term Savings Comparison
Investing in solar energy can lead to substantial long-term savings compared to traditional energy sources. Analyzing the financial impacts reveals the potential benefits of making the switch to solar.
On average, homeowners can save between $10,000 to $30,000 over 20 years by installing solar panels, depending on local utility rates and solar incentives.
By understanding your local electricity costs and solar incentives, you can estimate your potential savings. For instance, if your average monthly electricity bill is $150, you could save approximately $1,800 annually by going solar. Additionally, as electricity prices rise, the savings from solar energy will only increase over time, providing a hedge against future rate hikes.Implementing solar energy not only benefits your wallet but also contributes to environmental sustainability, making it a wise investment for the future.
Maintenance of Solar Panels
Maintaining solar panels is essential for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. Regular upkeep not only maximizes energy production but also extends the lifespan of the entire solar energy system. Proper maintenance can help identify and rectify minor issues before they develop into major problems, allowing homeowners to enjoy the benefits of clean energy with minimal disruptions.To keep solar panels in top shape, a few straightforward maintenance practices should be followed.
These include routine cleaning, inspections for damage, and monitoring system performance. By being proactive about maintenance, you can ensure that your solar panels operate efficiently. Here’s what you need to know:
Regular Cleaning
Keeping your solar panels clean is crucial, as dirt, dust, and debris can block sunlight and reduce efficiency. Here are some effective cleaning recommendations:
- Check the panels at least twice a year for dirt accumulation, especially after heavy rain or dust storms.
- Use a soft cloth or sponge with mild soap and water for cleaning. Avoid abrasive materials that could scratch the surface.
- For those hard-to-reach areas, consider hiring a professional cleaning service that specializes in solar panels.
Inspection for Damage
Regular inspections can help catch potential issues before they lead to costly repairs. Here’s a checklist for your inspection routine:
- Examine the panels for cracks or chips. Any physical damage may require immediate attention.
- Look for signs of corrosion on wiring or connectors, as this can impact performance.
- Ensure that there are no overhanging branches that may cast shadows on the panels.
Monitoring System Performance
Keeping an eye on your solar panel system’s performance can help identify any drop in efficiency. Consider the following:
- Regularly check the energy output through the inverter, which should display real-time data on energy production.
- Compare current energy output against historical data to notice any discrepancies.
- If performance drops significantly, consult with a technician to troubleshoot the issue.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Understanding common problems that can arise with solar panels can help in swift troubleshooting. Some typical issues include:
- Inverter issues: Check if the inverter is showing any error codes. Resetting the inverter may resolve minor glitches.
- Electrical connections: Loose or corroded connections can cause inefficiency. Ensure all connections are secure and clean.
- Shading: Regularly assess if new structures or trees are casting shadows on the panels that could affect energy production.
Maintenance Schedule
Establishing a regular maintenance schedule is key to keeping your solar energy system running smoothly. Here’s a suggested timeline:
- Daily: Monitor energy production via your inverter.
- Monthly: Visually inspect the panels for dust and debris.
- Bi-annually: Perform a thorough cleaning and detailed inspection for damage.
- Annually: Hire a professional to conduct a comprehensive system check and maintenance service.
By maintaining your solar panels regularly, you not only ensure their efficiency but also protect your investment in renewable energy.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Government incentives and rebates play a crucial role in making solar panel installation more affordable for homeowners and businesses. These financial incentives can significantly lower the initial costs, making solar energy a more viable option for many. Understanding the available incentives and how to apply for them can help you maximize your savings and reduce the overall investment required for solar panel systems.Various government incentives are available at both federal and state levels, aimed at promoting the adoption of renewable energy.
These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, grants, and other financial assistance programs. Below are some of the key incentives you should be aware of:
Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is one of the most significant incentives for solar panel installation. It allows homeowners to deduct a percentage of the cost of their solar system from their federal taxes. As of 2023, the ITC is set at 30% for systems installed after 2022, which can lead to substantial savings.
State-Level Incentives
In addition to federal incentives, many states offer their own programs. State incentives can vary significantly, so it’s important to check what is available in your area. Some common types of state incentives include:
- State Tax Credits: Some states offer their own tax credits that can be claimed in addition to the federal ITC, further reducing the overall tax burden.
- Rebates: Certain states provide cash rebates for the installation of solar systems, which can be applied at the time of purchase to lower the upfront costs.
- Performance-Based Incentives (PBIs): These are payments made to solar system owners based on the amount of energy produced by their solar panels over a specific period.
Applying for Incentives
Applying for these incentives typically involves a straightforward process, but it requires careful attention to detail. Here are the general steps you should follow:
1. Research Available Incentives
Start by researching federal, state, and local incentives that apply to solar panel installations in your area. Websites like the Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) can be a helpful resource.
2. Gather Necessary Documentation
When applying, you will need to provide various documents, such as proof of purchase, installation agreements, and sometimes energy production reports.
3. Complete Required Forms
Each incentive program will have its own application form. Ensure you fill out all forms accurately to avoid delays in processing.
4. Submit Applications
Follow the submission guidelines for your selected incentives, which may involve online submissions or mailing physical documents.
Impact on Overall Costs
Government incentives can significantly affect the overall costs of solar panel installation. For instance, without the ITC, a solar system costing $20,000 would still pose a considerable financial burden. However, with the ITC applied, the cost drops to $14,000, making solar energy far more accessible. Additionally, state rebates and tax credits can further diminish the investment required.In summary, taking advantage of government incentives and rebates can dramatically reduce the costs associated with solar panel installation.
By understanding the various programs available and how to apply for them, you can maximize your savings and make the switch to renewable energy an economically viable choice.
Future of Solar Technology

The future of solar technology is bright, with numerous advancements poised to redefine how we harness sunlight for energy. As the world shifts towards sustainable practices, innovative technologies are emerging, enhancing the efficiency and versatility of solar panels. This section explores the exciting developments in solar technology, from cutting-edge designs to smart home integrations.
Emerging Technologies in Solar Panel Design and Efficiency
Recent advancements in solar technology focus on enhancing the efficiency and aesthetic appeal of solar panels. Innovations like bifacial solar panels allow sunlight to be captured from both sides, significantly increasing energy generation. Another promising technology is the development of perovskite solar cells, which have demonstrated potential efficiencies exceeding 25%, compared to the traditional silicon-based panels that average around 15-20%.
Important improvements in solar panel design include thin-film technology, which offers lightweight and flexible options that can be integrated into various surfaces, such as rooftops or even clothing. These developments not only improve energy output but also pave the way for solar energy to blend seamlessly into everyday applications.
“The potential efficiency of perovskite solar cells is transforming the landscape of solar energy technology.”
Integration of Solar Energy into Smart Home Systems
The integration of solar energy systems into smart home technology marks a significant shift in energy management. Homeowners can now use solar energy in conjunction with smart devices to optimize energy consumption. Smart energy management systems can track energy usage patterns and automatically adjust power distribution in the home, prioritizing solar energy when available. Key benefits of this integration include:
- Increased Energy Independence: Homeowners can become less reliant on grid power by storing excess solar energy in home batteries.
- Cost Savings: Smart systems can reduce energy bills by optimizing the use of solar energy during peak hours.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Homeowners can monitor solar energy production and consumption in real-time through smartphone apps, leading to more informed energy usage decisions.
As smart home systems evolve, the synergy with solar technology will likely enhance user experience and energy efficiency, making it easier for individuals to manage their energy consumption sustainably.
Comparison of Traditional Solar Technology with Innovative Advancements
Traditional solar technology primarily relies on silicon-based solar panels, which, while effective, come with limitations related to efficiency and flexibility. In contrast, innovative advancements in solar technology are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in energy generation. Comparative highlights include:
| Aspect | Traditional Solar Technology | Innovative Advancements |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 15-20% | Up to 30% (perovskite cells) |
| Flexibility | Rigid panels | Flexible and lightweight options |
| Environmental Impact | Silicon extraction and processing | Lower impact materials, potential for recycling |
| Integration | Standalone systems | Seamless integration with smart homes |
The leap from traditional to innovative technologies in solar energy represents not just an evolution in design but a transformation in how we perceive and utilize solar power. As these advancements continue to proliferate, a more sustainable and energy-efficient future is on the horizon.
Real-Life Case Studies
Exploring real-life case studies of solar panel installations provides valuable insights into the practicality and effectiveness of solar technology. These examples demonstrate how various homeowners and businesses have successfully integrated solar energy solutions into their properties, showcasing the challenges faced and the benefits gained.
Residential Case Study: The Johnson Family
The Johnson family in California decided to install solar panels on their home to reduce energy costs and decrease their carbon footprint. Initially, they faced challenges concerning financing and selecting the right panel type. They opted for high-efficiency monocrystalline panels, ensuring maximum energy production even with limited roof space. Through extensive research and consultations with solar providers, they secured a combination of federal tax credits and state incentives, which significantly offset their installation costs.
The installation process was completed in just three days, with minimal disruption to their daily lives.The Johnson family now enjoys a 70% reduction in their electricity bills and has seen their property value increase due to the solar installation. Furthermore, they take pride in contributing to a more sustainable environment.
Commercial Case Study: GreenTech Innovations
GreenTech Innovations, a medium-sized tech company, decided to invest in solar energy to enhance their corporate sustainability image and cut down on operational costs. The primary challenge they faced was the initial investment and the suitable placement for the solar array within their urban setting.After conducting a thorough site assessment, they chose to install solar panels on their office building’s rooftop, which was strategically located to maximize sun exposure.
They collaborated with a solar developer who helped them navigate the complex financing options and tax incentives available for businesses.The installation took four weeks, and post-installation, GreenTech observed a 40% decrease in their monthly energy expenses. Additionally, their commitment to renewable energy attracted environmentally conscious clients and improved employee morale, reinforcing their brand’s positive image in the market.
Community Initiative: Solar for All Project
A community initiative called “Solar for All” aimed to provide solar panel installations to low-income families in a rural area. The primary challenge was securing funding and community buy-in. Organizers held workshops to educate residents about the benefits of solar energy, addressing misconceptions and concerns.Through partnerships with local non-profits and government grants, the project secured the necessary funding to install solar panels on 100 homes.
The installation process involved community volunteers and local businesses, fostering a sense of unity and shared purpose.Post-installation, families reported an average of 60% savings on their monthly utility bills. The environmental benefits were also significant, as the project collectively reduced carbon emissions equivalent to planting over 1,000 trees. Community members expressed pride in their contribution to sustainable energy and environmental stewardship.
These case studies exemplify the transformative potential of solar energy, showcasing not only the practical benefits of reduced energy costs but also the broader impact on community engagement and sustainability.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, diving into Solar Panel Installation can transform your approach to energy consumption. With various types and financing options available, as well as government incentives, making the switch has never been easier. By investing in solar technology, you not only contribute to a greener planet but also set yourself up for long-term savings and energy independence.
Quick FAQs
How long does a solar panel installation take?
Typically, a residential solar panel installation can take one to three days, depending on the size of the system and weather conditions.
Do solar panels work on cloudy days?
Yes, solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, though at reduced efficiency compared to sunny days.
What maintenance do solar panels require?
Solar panels require minimal maintenance, such as regular cleaning to remove dirt and debris, and periodic inspections to ensure they are functioning properly.
Can I install solar panels myself?
While some skilled DIYers may attempt it, it’s best to hire professionals for safety and to meet local regulations and warranties.
What happens to solar panels at the end of their life?
Most solar panels can be recycled, and manufacturers are increasingly working on sustainable disposal methods to minimize waste.